Genetic disorders related to organelle function
Highlighted Points
- diseases associated with specific cell-organelles.
- cell organelles and diseases
- genetic disorders and organelles worksheet answers
- lysosomes
- lysosomes and pompe disease
- genetic disorders and organelles worksheet answers
- diseases that affect cellular structures or functions
- diseases of the cell
Genetic disorder
A genetic
disorder is a condition caused in whole or in parts by a shift in the sequence
of DNA. Genetic abnormalities can be caused by a mutation in one gene, or by
mutation in several genes, or can be caused by the combination of gene mutation
and environmental factor.
Some of the genetic disorders related to organelles functioning are as given below.
1.
Kartaneger syndrome ( Cilia ):
This syndrome was first identified by Siewart in 1904. But the ethological link was first recognized by a scientist namely Kartaneger and reported 4 cases in 1933. This is an autosomal recessive hereditary ciliary disorder. This causes main problem in the movement in cilia, this may lead to chest infection, ear, mouth, and nose and infertility symptoms.
The disorders
related to ciliary motility may be acquired and congenital. The infertility
caused by KS patients in both male and females may be due to diminished sperm
motility and due to defective ovum in case of females.
Treatment:
Till know there
is no treatment for this condition. However treatments varies this is dependent
on the symptoms and signs present in each person but can also include the
therapy and antibiotics.
2. I - cell disease ( Golgi body ) :
This disease was first identified in 1967 by DE MARS and Leroy . This I - cell disorder is caused due to the mutation in the GNPTAB gene that inturn contributes to a problem in the UDP- acetyl glucoSamine- 1 - phosphotransferase enzyme. This disorder is a recessive autosomal genetic trait. This disease is also named as mucolipidiosis II ( ML II ).
This disease can impact on many body parts, but this can trigger
mental retradation and skeletal problems in body parts. In case of childrens
this may cause underweight at birth and creates many prolems in childrens.
Diagnosis:
This disease can be diagnosed before birth by using the chorionic villus or amniocentesis samplig procedure. In case of amniocentesis sampling we use amniotic fluid that surrounds the foetus.
The life expectancy of children with this disease is low & death can also occur between the fifth and seventh year.
Treatment:
The treatment of I- cell disease is supportive & also used
bone marrow transplantation can be used to correct the neurological
deterioration. However antibiotics are also administered at times. Any times
Physical threapy are provided in order to preserve joint function &
mobility.
3.
MELAS
Syndrome ( Mitochondria ) :
MELAS stands for Mitochondria encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis and stroke - like episodes. The diagnosis of MELAS is normally suspected on clinical grounds. However, confirmation of the diagnosis normally includes a muscle or brain biopsy. This condition is caused by the mutations in the dna of mitochondria organelle, so this is a maternally inherited since the mtdna is primarily present in ovum of dad. The occurrence is 1 : 4000 according to studies performed by scientists. However this condition affects both in males and females. In case of males they are lost by fertilization.
Signs and symptoms:
This disorder affects many parts of the body systems this include nervous system and even some parts of brain. Mostly this condition occurs in infancy after a time of normal development and Symptoms mainly appears at an age of 2 and 10 years old.
Treatment:
Untill there is no curative treatment available for this syndrome. However some drugs such as anti- convulsant are used in order to control MELAS syndrome.
4.
Treacher -collins syndrome ( Ribosomes ) :
This syndrome is also called as mandibulo facial dysostosis, Fraceschetti - ZwalenSyndrome.This is a genetic disorder that affects on the developnment of bones and other tissues of the face. In this syndrome the facial bones mainly cheek bones are underdeveloped this issue may lead to life threatening respiratory problems. In some cases the jaw and chin is very small. However this may causes hearing loss an Formation of cleft palate.
Causes :
This is mainly caused due to the mutations in the
genes like TCOF1, POLR1C, POLR1D that
causes treacher - collins syndrome. These genes play important role in the
developnment of the bones and tissues of
the face. They also plays a very important role in the producation of
ribosomal RNA.
Affected populations :
This affects equally both in males and females.
The prevalence ratio is 1: 10,000 - 50000 individuals in the population.
Clinical testing:
X - ray studies will confirm the extent of certain observed crainofacial problems. The test shows the smallness of the jaw( micrognathia ) and underdevelopment of the lower jaw bone ( mandibular hypoplasia ).
Treatment :
There is no treatment for TCS. However some times plastic surgery,
orthodontics are done in order to correct facial structure.
5. Lysosomal disorders and pompe disease :
LSDs are
inherited disorders resulting from a lack of specific enzymes that break down
certain lipids or carbohydrates in the
body cells.
If a person does not have enough of one of these enzymes, the body cannot break down the fat or carbohydrate targeted by enzymes for recycling. These fats or sugars accumulate in cell lysosomes where enzymes are active, disrupting normal function and causing lysosomal storage disorders.
Some of the most common lysosomal storage
disorders include:
1. Gaucherdisease: Gaucher disease often causes liver enlargement.
2. Niemann-Pickdisease: Similar to Gaucher disease, Niemann-Pick disease involves organ enlargement, lung dysfunction and central nervous system damage for certain subtypes.
3. Huntersyndrome: This disease is part of a group of disorders that cause bone and joint deformity as well as interference with normal growth.
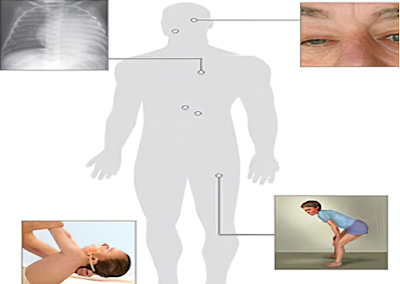
4. Glycogen storage disease II (Pompedisease) : Depending on the specific subtype, Pompe disease may cause heart enlargement and heart failure in case of infants. But in case of adults this may cause respiratory problems and severe muscle weakness.
5. Fabrydisease: This disorder often
causes severe burning pains in hands and feet in some cases, this may also cause
distinctive skin rash on the legs.
Pompe disease:
It is the first recognized
lysosomal storage disorder and the first neuromuscular disorder for which a
therapy (enzyme replacement) has been approved. The GAA enzyme hydrolyses glycogen to glucose in the
academic medium. When the GAA enzyme does not work properly this will lead to
the glycogen accumulation within and concomitant enlargement of this organelle
Pompe
disease, an inherited deficiency of lysosomal acid α-glucosidase (GAA), is a
severe metabolic myopathy with a wide range of clinical manifestations. Since the introduction of the therapy, the
overall understanding of the disease has progressed significantly, but the
pathophysiology of muscle damage is still not fully understood. The emerging
complex picture of the pathological cascade involves disturbance of calcium
homeostasis, mitochondrial abnormalities, dysfunctional autophagy, accumulation
of toxic un degradable materials, and accelerated production of lipofuscin
deposits that are unrelated to aging.
Causes:
Mutations
in the GAA gene prevent acid alpha-glucosidase from breaking down
glycogen effectively, which allows this sugar to build up to toxic levels in
lysosomes. This buildup damages organs and tissues throughout the body, particularly the muscles, leading to the
progressive signs and symptoms.








No comments:
Post a Comment