Blockchain Technology future, impacts and ethical concerns
Introduction of
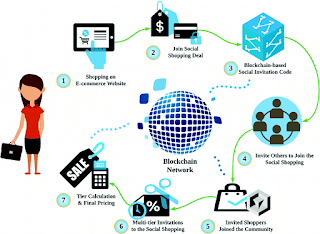
Blockchain
technology is a data storage system that makes it incredibly difficult
and impossible, to alter, hack, or exploit the system (Vivekanadam, 2020). Blockchain
technology is essentially a shared ledger of transactions that is duplicated
and distributed through the entire network of operating networks that make up
the block-chain (Chauhan & Ramaiya).
Why I care about
Blockchain
technology has the potential to be applied to a variety of industries due to
its decentralization, immutability, stability, compliance, and permanency
flexibility for recordkeeping (Venkatesh, Kang, Wang, Zhong, & Zhang, 2020). Blockchain
also can be used for identity authentication, infinite scalability,
systems integration, and other uses. Blockchain technology still has not
reached its full potential to empower the current trends (Bouachir, Aloqaily, Tseng, & Boukerche, 2020).
Future of Blockchain technology
Blockchain
technology has been one of the most highly discussed digital technologies and practices
in recent years. Blockchain is a digital data management infrastructure
for both stable and flexible bigdata (Deepa et al., 2020). Blockchain
technology can be used to store ehealth data (Nandakumar & Clement, 2020). Through
overcoming the inadequacies of open networks and decentralization, block-chain
technology has the power to change the world throughout the future. Through implementing blockchain, every business is
expected to improve its operations to unprecedented level (Bouachir et al.,
2020).
At least one innovative Blockchain-based enterprise will be estimated $10
billion by 2022. By 2030, the value of the Blockchain network will have grown
just to above $460 billion, and by 2040, it'll have increased to over $6.1
trillion.
Blockchain technology impacts and
ethical concerns
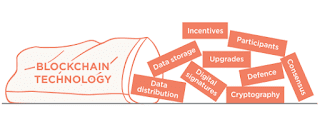
Blockchain
technology offers additional efficiency (potentially), reliability, protection,
and integrity by minimizing the risk (and friction) correlated with relying on
either one or a few networks of authorities (Kayıkcı, 2021). Indeed, the
intrinsically "anti-authoritarian" essence of the Blockchain network
contributes to its sustainability. The first ethical issue that supporters of
Blockchain must overcome is not reporting features technology's capabilities
and therefore over-promising in terms of what it can provide. The two most serious ethical concerns about block-chain
technology are 1) its environmental consequences and 2) its ability to promote
illegal activity. I'm also aware that, as I stated earlier in this article
while explaining how to understand Blockchain, the technology is powered by
sheer computational power. In terms of resource utilization and scaling, the
new Blockchain technology is inefficient. The root ethical issue is that
virtually all would be involved in blockchain activities and require a backup
of the key block-chain (Hanees & Manikandan, 2020).
Why the rest of us should care
Blockchain
is a cutting-edge technical innovation that can help in recordkeeping because
of its accuracy and constancy. Anyone wanting to validate a particular
transaction would technically be able to do so since a Blockchain lists the
entire ledger of transactions. The key benefits of blockchain technology are decentralization,
immutability, reliability, and accountability. The use of blockchain
technology allows for authentication without the need for third-party
verification. The data structure in a Blockchain is append-only, which means
the information can't be modified or deleted (Guo, Xie, & Li, 2020). Block-chain
technology is only in its early stages and has potential to do a great deal of challenges
in the world. Blockchains now have to deal with five big issues like security,
confidentiality, regulatory, legal, and ethical considerations, but in future Blockchains
can used for very complex data (Venkatesh et al., 2020).
References (APA Style)
Bouachir, O., Aloqaily, M., Tseng, L., & Boukerche, A. (2020). Blockchain and fog computing for cyberphysical systems: The case of smart industry. Computer, 53(9), 36-45.
Chauhan, C., & Ramaiya, M. K. Review the Security Improvement Technique for Industry 4.0 Using Block Chain Technology.
Deepa, N., Pham, Q.-V., Nguyen, D. C., Bhattacharya, S., Prabadevi, B., Gadekallu, T. R., . . . Pathirana, P. N. (2020). A survey on blockchain for big data: Approaches, opportunities, and future directions. arXiv preprint arXiv:2009.00858.
Guo, L., Xie, H., & Li, Y. (2020). Data encryption based blockchain and privacy preserving mechanisms towards big data. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 70, 102741.
Hanees, A., & Manikandan, S. (2020). Block chain technology: myths, ethics and current trends in it and Ides.
Kayıkcı, Y. (2021). Blockchain in SCM: The Impact of Block Chain Technology for SCM-Potentials, Promises, and Future Directions. Logistics 4.0, 146.
Nandakumar, R., & Clement, C. (2020). A Review on Block Chain Technology Applications with an Emphasis on Health Care.
Venkatesh, V., Kang, K., Wang, B., Zhong, R. Y., & Zhang, A. (2020). System architecture for blockchain based transparency of supply chain social sustainability. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 63, 101896.
Vivekanadam, B. (2020). Analysis of Recent Trend and Applications in Block Chain Technology. Journal of ISMAC, 2(04), 200-206.
About Author
Mr. Imran Zafar
has completed his Bachelor of Science (BS) degree in Bioinformatics from
COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Islamabad Sahiwal campus under
supervision of Dr. Ahmad Ali, Bachelor of education (B.ed) from Allama Iqbal
Open University (AIOU) and Master of Science (MS) in Bioinformatics from
Department of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology, Virtual University of
Pakistan, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan under supervision of Dr. Muhammad Tariq
Pervez. For research work during BS and MS he has also done internships from
School of biological Science (SBS), University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences
(UVAS) and Center of Excellence in molecular biology (CEMB) Lahore. He has published
several research articles and book computers in reputed journals recognized from
Higher Education Commission (HEC) of Pakistan.
His research is mainly focused on the field of Bioinformatics, Genomics,
Computational Biology and Molecular Biology in the domain of life science to
performed computational analysis. He is now working in Ministry of Education as
a Science subject instructor in the Department of Education Punjab,
Pakistan.








No comments:
Post a Comment